Homepage
Contact

Jian Wang
I am actively seeking a research scientist/engineer position :)
Max-Planck-Institut für InformatikDepartment D6: Visual Computing and Artificial Intelligence
| office: |
Campus E1 4,
Room 117 Saarland Informatics Campus 66123 Saarbrücken Germany |
| email: | jianwang AT mpi-inf.mpg.de |
| phone: | +49 681 9325 4044 |
| fax: | +49 681 9325 4099 |
Research Interests
- Ego-centric Motion Capture
- Computer Vision
Publications
 |
Egocentric Whole-Body Motion Capture with FisheyeViT and Diffusion-Based Motion Refinement. Jian Wang Zhe Cao Diogo Luvizon Lingjie Liu Kripasindhu Sarkar Danhang Tang Thabo Beeler Christian Theobalt CVPR, 2024 [Arxiv] [Project Page] |
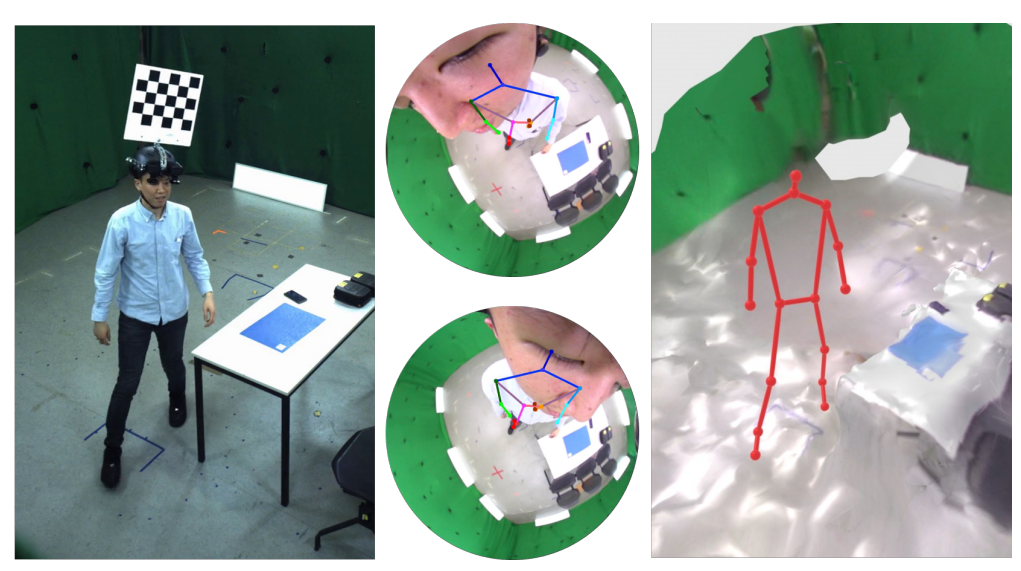 |
3D Human Pose Perception from Egocentric Stereo Videos. Hiroyasu Akada Jian Wang Vladislav Golyanik Christian Theobalt CVPR, 2024 [Arxiv] [Project Page] |
 |
EventEgo3D: 3D Human Motion Capture from Egocentric Event Streams. Christen Millerdurai Hiroyasu Akada Jian Wang Diogo Luvizon Christian Theobalt Vladislav Golyanik CVPR, 2024 [Project Page] |
 |
Scene-aware Egocentric 3D Human Pose Estimation. Jian Wang Diogo Luvizon Weipeng Xu Lingjie Liu Kripasindhu Sarkar Christian Theobalt CVPR, 2023 [Arxiv] [Project Page] |
 |
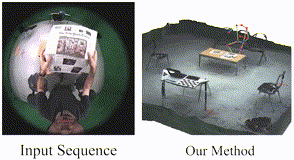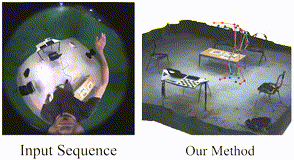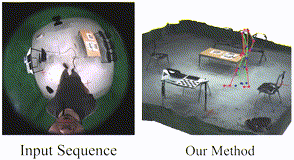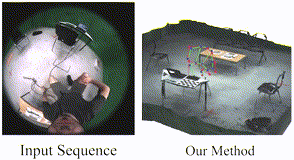
UnrealEgo: A New Dataset for Robust Egocentric 3D Human Motion Capture. Hiroyasu Akada Jian Wang Soshi Shimada Masaki Takahashi Christian Theobalt Vladislav Golyanik ECCV, 2022 [Project Page] |
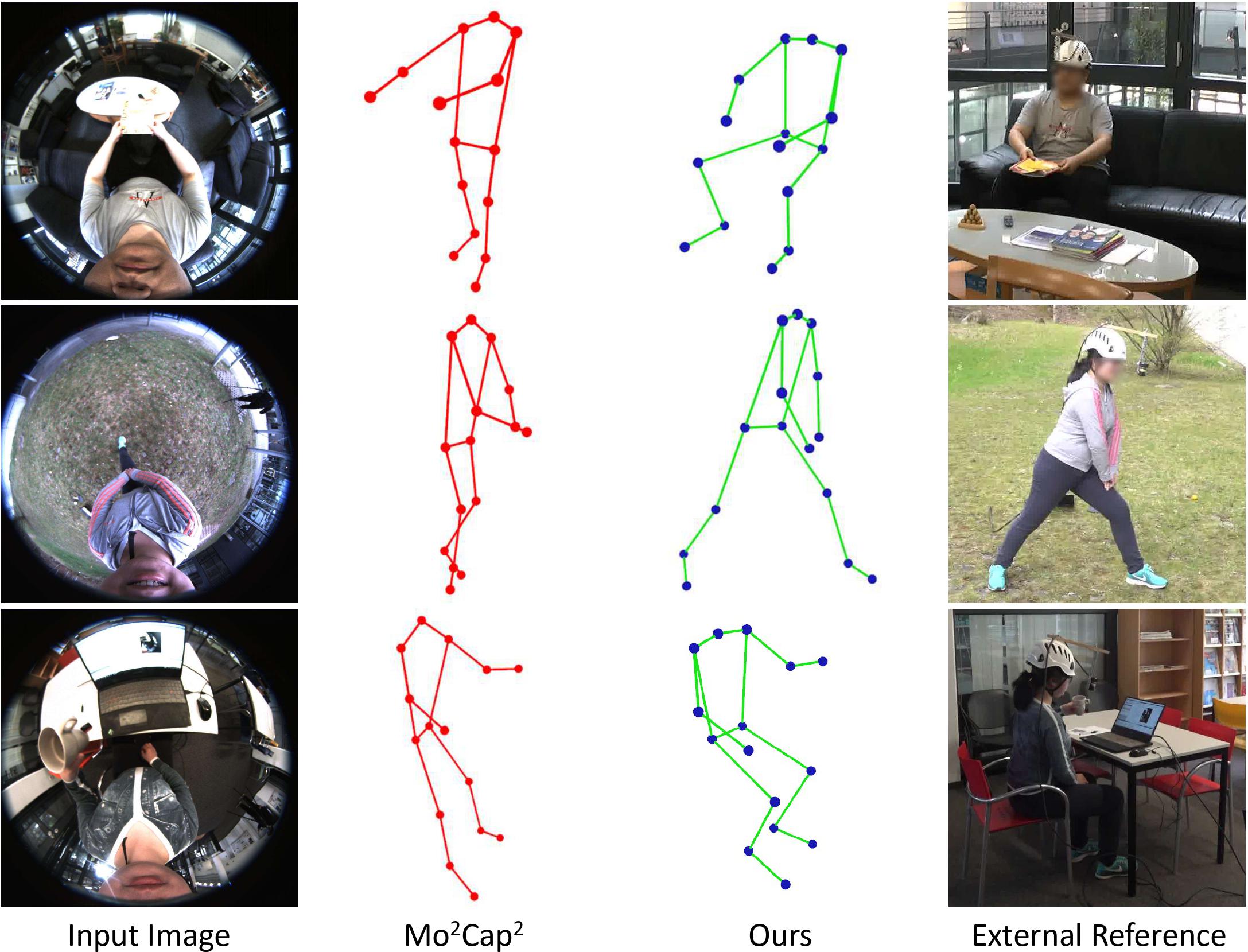 |
Estimating Egocentric 3D Human Pose in the Wild with External Weak Supervision. Jian Wang Lingjie Liu Weipeng Xu Kripasindhu Sarkar Diogo Luvizon Christian Theobalt CVPR, 2022 [Project Page] |
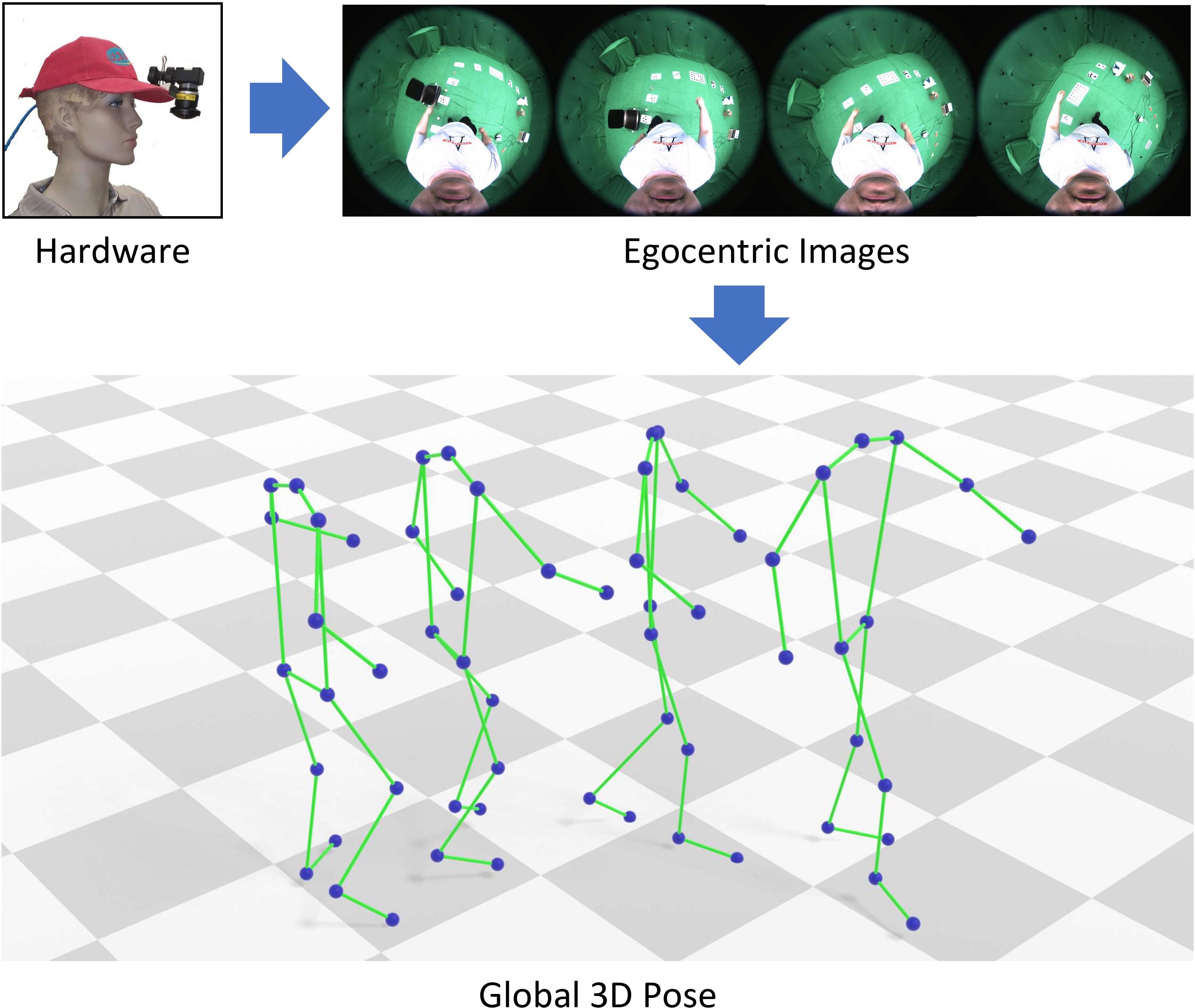 |
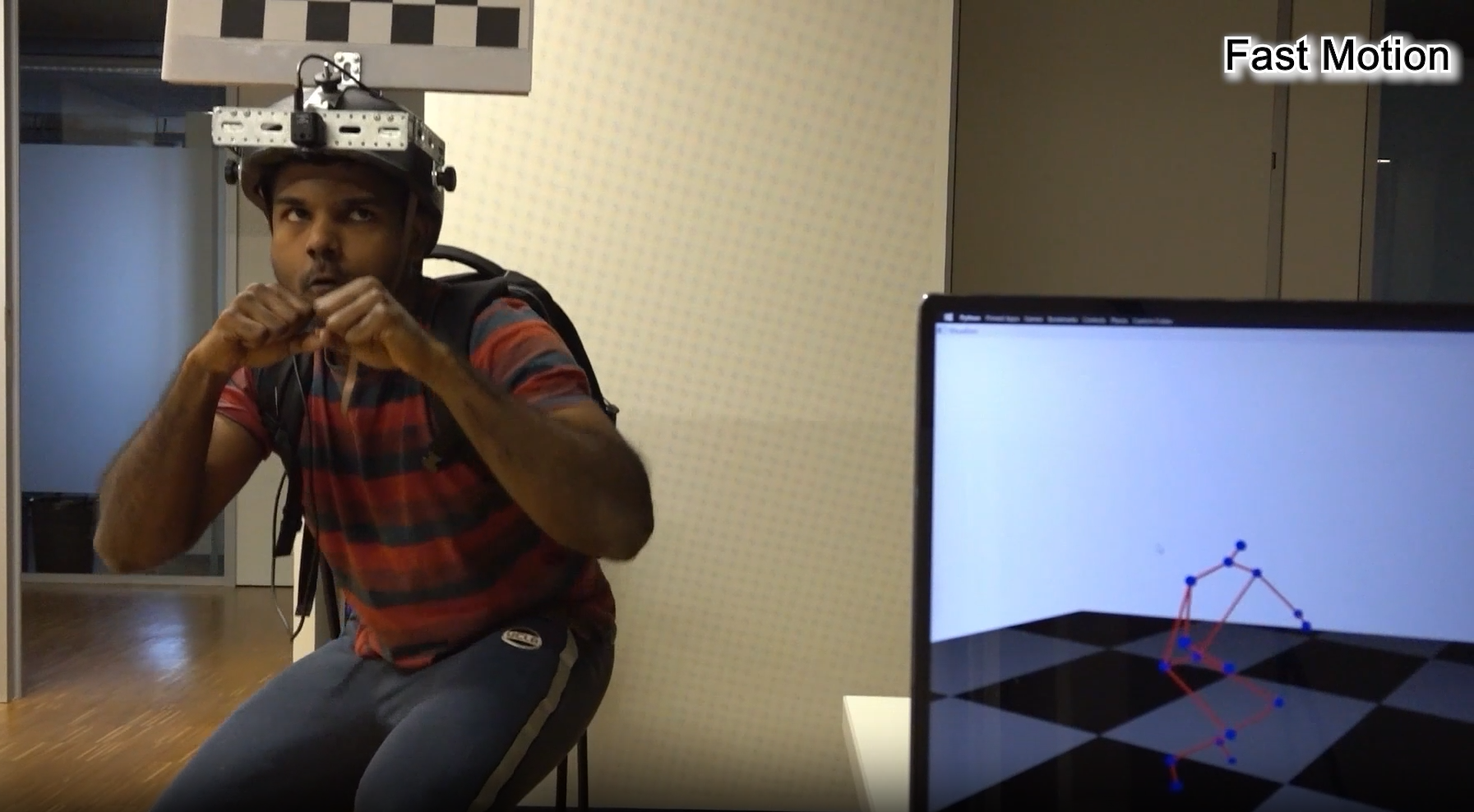
Estimating Egocentric 3D Human Pose in Global Space. Jian Wang Lingjie Liu Weipeng Xu Kripasindhu Sarkar Christian Theobalt ICCV(Oral), 2021 [PDF] [Supplementary Materials] [Video] [Project Page] |
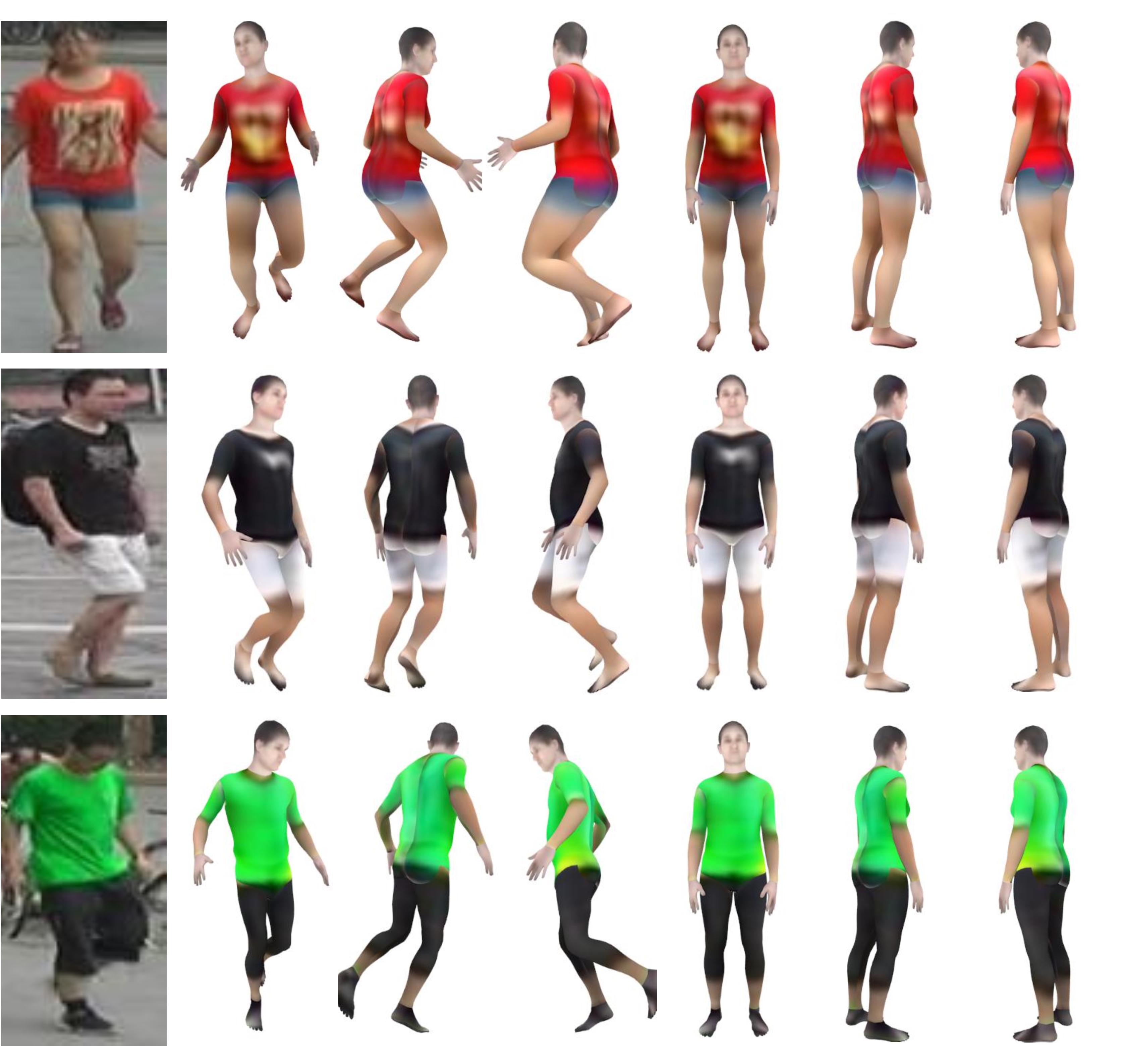 |
Re-Identification Supervised Texture Generation. Jian Wang Yunshan Zhong Yachun Li Chi Zhang Yichen Wei CVPR, 2019 [PDF] [Code] |
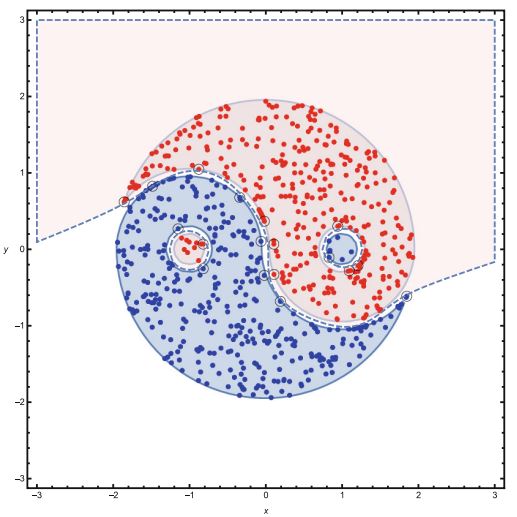 |
NIL: Learning Nonlinear Interpolants. Mingshuai Chen Jian Wang Jie An Deepak Kapur Naijun Zhan CADE, 2019 [PDF] [Code] |
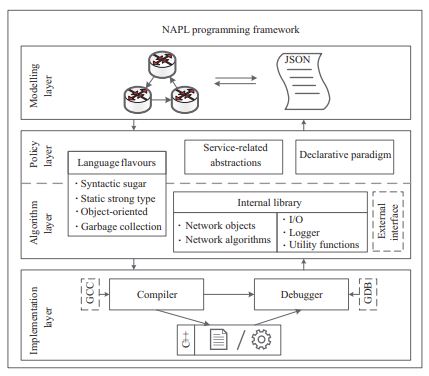 |
From Model to Implementation: A Network-Algorithm Programming Language.
Jian Wang
Jie An
Mingshuai Chen
Naijun Zhan
Lulin Wang Miaomiao Zhang Ting Gan SCIENCE CHINA Information Sciences, 2019 [PDF] |
Academic Service
- Conference refereeing:
CVPR 2022, ECCV 2022, TASE 2019, RTCSA 2019
Teaching
- Summer semester 2022, 2021:
Supervisor for Computer Vision and Machine Learning for Computer Graphics Seminar, Saarland University and MPI for Informatics
Education
- April 2020 - present:
Ph. D. student in Computer Science at the Universität des Saarlandes, Saarbrücken, Germany and the Max-Planck-Institut für Informatik
- September 2016 - July 2019:
Master Student in Computer Science at the Institute of Software, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
- September 2012 - July 2016:
Bachelor Student in Chemistry at the Peking University.